Quick Guide to IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS
Almost everything you need to know about the primary as-a-service cloud computing business models.
Almost everything you need to know about the primary as-a-service cloud computing business models.
Start typing to search...
As-a-service (-aaS or AAS) are business models in which something is provided to customers (either internally or externally) as a service. Primarily, AAS offerings are focused on services delivered via the cloud. In this blog, we’re only going to explore three types of AAS offerings, but many more exist, including:
For a near complete list of AAS offerings, check out this big -aaS list from Ryan LaFlamme.
IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS are cloud computing services that offer an alternative to on-premise IT solutions (where data, apps, and software run on in-house computer servers). On-premise (or on-prem) solutions are a rarity nowadays, but think of the olden days of Adobe InDesign on CD-ROM.
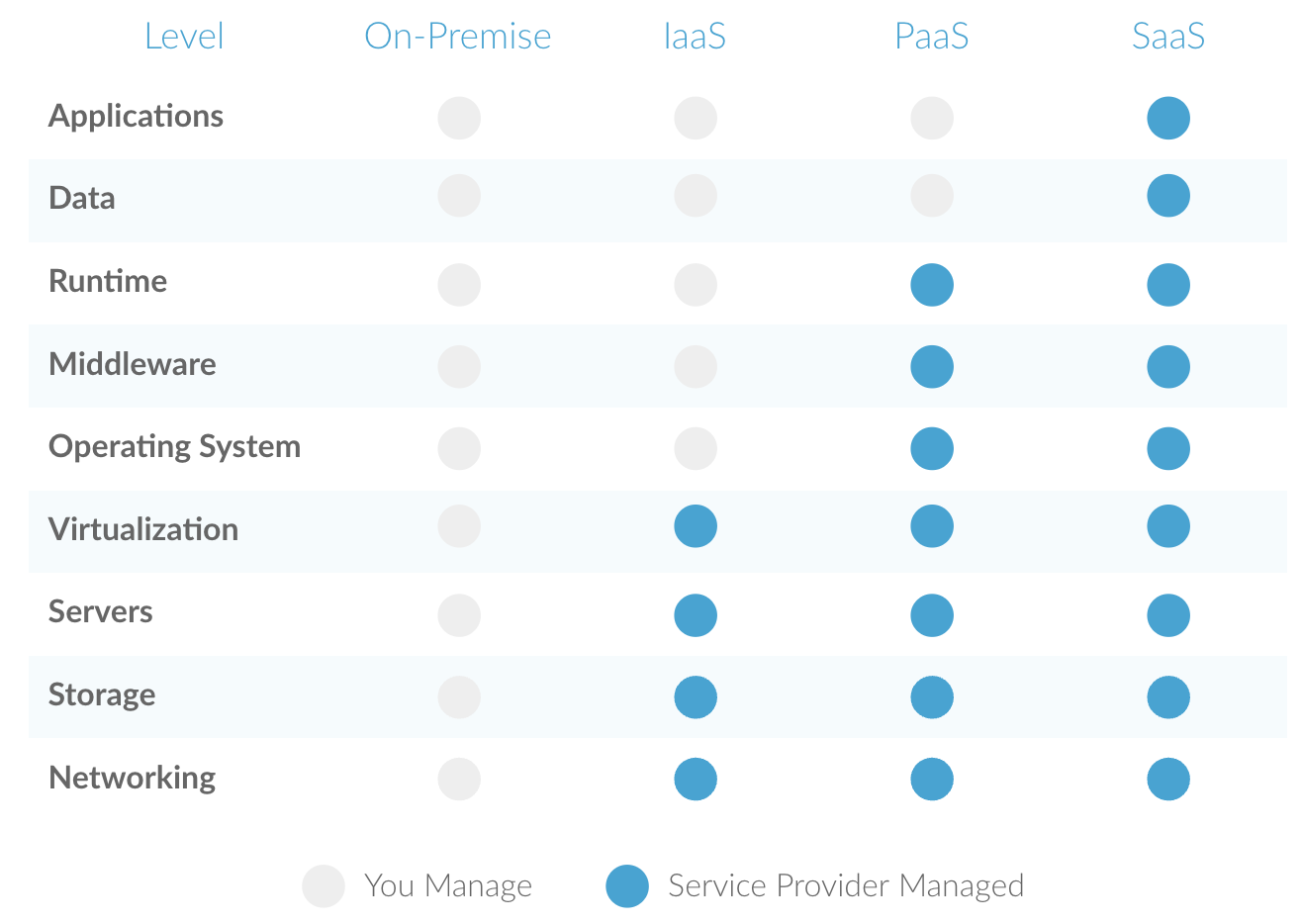
The graphic below provides a high-level overview of the primary differences between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS from an IT perspective (i.e., this is primarily for the techies. All others to see layman's terms below).
What is IaaS? |
IaaS is a type of cloud computing that provides users with access to computing resources, like servers, storage, and networking. It allows users to rent these resources on a pay-as-you-go basis, so they don't need to invest in hardware or software upfront. IaaS customers have full control over the virtual machines and can install and configure their own software and applications. |
Who uses IaaS? |
|
What are examples of IaaS? |
|
What are the benefits of IaaS? |
|
What are the limitations of IaaS? |
|
What is PaaS? |
PaaS is a cloud computing model in which customers can develop, run, and manage web applications without having to worry about the underlying infrastructure. PaaS provides customers a platform to build and deploy applications quickly and easily. |
Who uses PaaS? |
|
What are examples of PaaS? |
Sitecore's PaaS Products:
|
What are the benefits of PaaS? |
|
What are the limitations of PaaS? |
|
What is SaaS? |
SaaS is a cloud computing model in which software applications are hosted on a remote server, and customers access them through a web browser. SaaS eliminates the need for customers to install and manage the software on their own systems. |
Who uses SaaS? |
|
What are examples of SaaS? |
Sitecore's SaaS Products: |
What are the benefits of SaaS? |
|
What are the limitations of SaaS? |
|
Each cloud computing model provides different levels of access to cloud resources and capabilities and can be used for different types of applications. As each serves a distinct purpose, it's essential to determine your business needs to ensure your chosen cloud services provide value.
Have any questions regarding Sitecore’s SaaS and PaaS products? Let us know.